Did you know that heartburn, anxiousness, irritability, depression and weight gain can be long-term problems set in motion by a simple childhood concussion? Whether it happened to your child a year ago, or the injury happened to you 20 + years ago, there are some things you should know about the lingering effects of concussion damage.
Did you know that heartburn, anxiousness, irritability, depression and weight gain can be long-term problems set in motion by a simple childhood concussion? Whether it happened to your child a year ago, or the injury happened to you 20 + years ago, there are some things you should know about the lingering effects of concussion damage.
According to the CDC annual visits to the emergency room for concussions increased from 153,375 to 248,418 from 2001 to 2009. The most common patient is a young male between 10-19 years old and many of these injuries are the consequence of playing sports.
A concussion is injury to the brain from a mechanical force that strikes the skull. The skin or the bone of the skull may remain intact but the shockwave penetrates and damages cells of the brain. Helmets may protect against skull fractures but do nothing to prevent concussions.
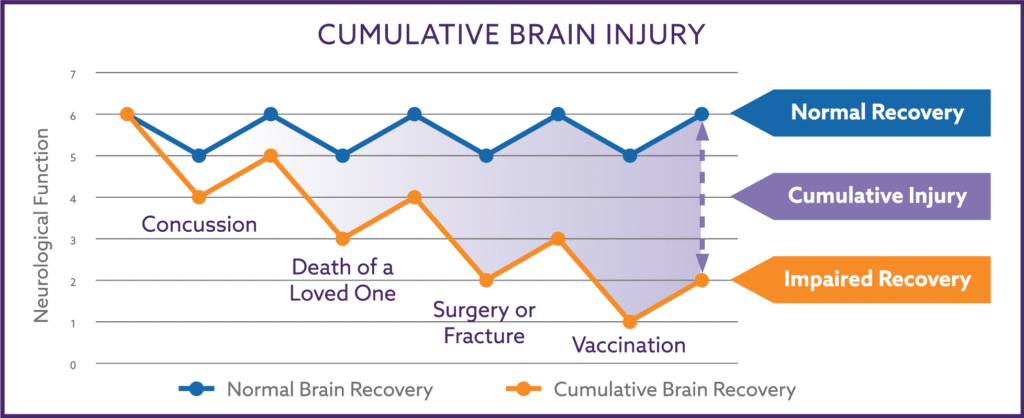
The damage from concussion can be substantial and long lasting even if an MRI test or CT scan result is “normal”. Permanent neurological damage can occur even if the individual is not knocked unconscious from the injury, and upwards of 20% of individuals have measurable damage to their autonomic nervous system 12 months after the injury.
Kids and adults respond differently to concussions. Kids are more likely to develop a concussion, take longer to recover, and more frequently have long-term neurological and cognitive effects. Kids who suffer from a concussion should be followed up and evaluated by a physician specializing in concussion management. Improper management of a concussion injury can lead to slower recovery or long lasting symptoms.
After the injury, physical and mental rest is essential for the brain to heal rapidly and completely. Depending on the severity of the concussion, kids should be kept home from school and not engage in any focused mental activity (video games, studying) following a concussion. They should not rapidly return to playing sports even if the overt symptoms (headaches, poor balance) have resolved. Being too active after the concussion prolongs recovery time and increases the likelihood of developing chronic problems.
After the initial headaches resolve, patients often have more subtle neurological damage that can result in occasional lightheadedness, heartburn, frequent urination, worsening school performance, anxiousness and irritability, depression and weight gain.
If you or your child suffers a concussion, make sure you seek out a physician specializing in the autonomic nervous system for a thorough evaluation. There are tools to accurately diagnosis and treat the lingering damage caused by concussions and often result in a complete recovery.
© 2014. Dr. Patrick M. Nemechek. All Rights Reserved.